Despite statistics demonstrating the importance of cloud computing in business, like its business efficiency, cost-benefits, and competitive advantages, a sizable portion of the corporate community continues to operate without it.
According to a study conducted by the International Data Group, 69 percent of businesses already use cloud technology in some capacity, and 18 percent plan to do so in the future. Organizations that focus on big data, cloud, mobility, and security, create income 53 percent faster than their competitors.
These figures show that an increasing number of tech-savvy businesses and industry executives recognize the cloud computing trend’s multiple benefits. But they’re also using technology to run their businesses more efficiently, provide better customer service, and boost their profit margins.
Most people already use cloud computing services like Google Drive and TurboTax without realizing it. Cloud-based applications include Facebook and Instagram. They’re useful for companies that need to access big volumes of data through a secure web network.
Still, some executives are cautious about committing to cloud computing solutions for their companies. If you are one of those technocrats, this blog is for you as we have listed down the key importance of cloud computing in business that your organization can benefit from.
But first, let’s start from scratch. To do so, we need to know the basics of cloud computing, and that’s exactly what we will see next.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing offers computer services over the Internet (“the cloud”) to provide faster innovation, more flexible resources, and economies of scale. You usually only pay for the cloud services you use, which helps you cut expenses, manage your infrastructure more effectively, and scale as your business grows.
Why cloud computing in business?
There are multiple reasons why cloud computing is so important in today’s day and age. I’ve come up with a few things that will assist in giving rationale without getting into too much detail:
- One of the main reasons why many small and large company sectors worldwide are now embracing the cloud is its enormous cost-cutting potential. Yes, cloud computing has drastically reduced the cost of hardware, software, and other server resources.
- Instead of employing physical gear and software, we may execute our workload data, applications, and processes remotely over the internet.
- Cloud computing service providers handle day-to-day difficulties such as server maintenance, software/hardware installation, and license renewal.
- With the aid of the cloud, we may access any data or apps through the internet anytime and wherever we want. Installing and updating 100 pre-configured programs is possible.
- Cloud stores data remotely, protecting and restoring any crashed or lost data, so we don’t have to be concerned about data loss or corruption. It also provides excellent security.
With the advent of new cloud computing technologies, several providers offer access and payment options based on usability. Users may switch programs based on their needs and utilizing resources. Ideally suited to expanding businesses with high bandwidth demands. Cloud computing may help you save both time and money.
What are the benefits/importance of cloud computing in business?
Flexibility
Companies that engage in cloud-based services benefit from a high level of flexibility. Cloud servers provide almost limitless bandwidth and storage capacity, allowing organizations to scale up and down their resources in real time as they grow and deal with increased website traffic.
This eliminates the requirement for on-site equipment and updates to be purchased and installed.
Employees may access programs and data stored on a remote server off-site, anywhere, and anytime, as long as an internet connection is accessible, thanks to cloud computing.
Continuity of Operations
Businesses can ensure dependable disaster recovery and backup solutions without the effort of putting them up on a physical device by investing in cloud computing. Investing in elaborate disaster recovery strategies may be pricey for many firms, and backing up data takes time. The cloud is built to replicate data saved across servers, ensuring it is promptly backed up if one fails. After a breakdown, immediately retrieving data again reduces website downtime and productivity loss.
Cost-effectiveness
Among the major benefits of cloud computing is the reduction of IT operations costs. Remote servers require no in-house storage, application needs, and the costs associated with software upgrades, maintenance, and data storage. Cloud-based services also tend to be less expensive because they are often provided on a pay-per-use basis, which means businesses can rent only what they need while ensuring a return on investment. Cloud computing has many advantages for small and medium-sized businesses with limited budgets.
Improvised Collaboration
Collaboration between groups and communities with access to the same files has improved significantly in the cloud environment. It eliminates the communication limits of traditional IT models, allowing employees working in disparate places to access information and engage with team members and important individuals much more quickly and easily. This streamlines operation and allows more work to be completed quickly.
Scalability and Performance
Cloud technology is designed to scale to suit a company’s changing IT demands. More storage space and bandwidth will be required to keep up with the increased traffic to the website. Cloud servers can be automatically deployed to assist businesses in scaling up and down. Cloud technology speeds up websites and reduces downtime.
Friendly to the Environment
Cloud-based services are ecologically beneficial for firms with a CSR who want to keep their carbon impact low. When data is stored, the workplace consumes less energy and emits fewer carbon emissions, and online applications are performed in a pay-per-use virtual environment. Cloud computing also minimizes the demand for the actual hardware, requiring less IT equipment in the office.
Software Updates on Demand
Many cloud service providers provide regular system updates to meet IT needs consistently. They take care of cloud server maintenance, including security upgrades, 24 hours a day, seven days a week, saving organizations time and money. According to research, businesses in the United Kingdom spent 18 working days per month managing their on-site IT security in 2010.
Integration of software that is done automatically
Businesses will no longer need to integrate their applications manually. Software applications and services can be quickly and easily customized using cloud technology, allowing businesses to handpick the best services.
What are the different types of cloud computing?
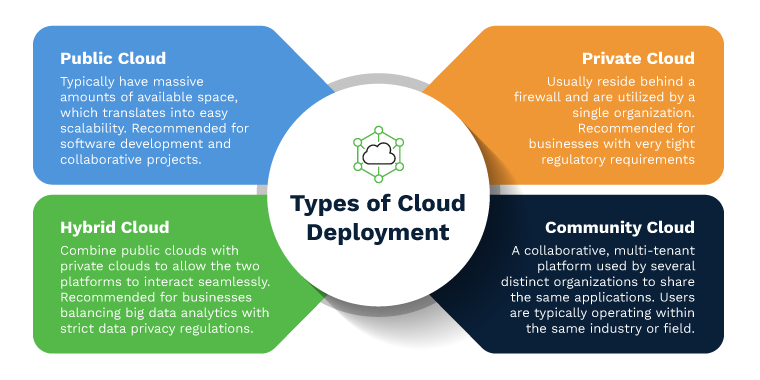
Now that we have seen the importance of cloud computing in business let’s take a quick look at the different types of cloud computing that are out there and see how each one is different from one another so that you can choose the best kind of cloud technology for your business requirements.
The four basic forms of cloud computing are private, public, hybrid, and multi-cloud. Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platforms-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service are the three main types of cloud computing services (SaaS).
What’s the difference?
Location and ownership used to be the easiest ways to distinguish between public clouds, private clouds, hybrid clouds, and multi-clouds. But it’s no longer that straightforward. As a result, there are multiple limitations to consider as we evaluate the differences below.
- Public Clouds
Public clouds are cloud environments often built using IT infrastructure that does not belong to the end user. The most popular public cloud providers are Alibaba Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
Traditional public clouds were always hosted off-site. However, today’s public cloud companies are beginning to offer clients’ data centers cloud services. Location and ownership differences have become outdated as a result of this.
When partitioned and dispersed to several tenants, all clouds become public clouds. Because some cloud providers (such as the Massachusetts Open Cloud) enable tenants to utilize their clouds for free, fee structures are no longer required aspects of public clouds. Public cloud providers’ bare-metal IT infrastructure can be abstracted and sold as IaaS or built into a cloud platform and sold as PaaS.
- Private Clouds
Private clouds are cloud environments dedicated to a single end-user or group and often hosted behind that user’s or group’s firewall. All clouds become private when the underlying IT infrastructure is devoted to a single client with complete remote access.
However, private clouds are no longer limited to on-premises IT infrastructure. Organizations are already constructing private clouds on rented, vendor-owned data centers off-site, obviating the need for any location or ownership regulations. As a result, a variety of private cloud subtypes have emerged, including:
- Private clouds that are managed
Customers establish and utilize a private cloud that a third-party provider deploys, configures, and manages. Managed private clouds are a cloud delivery alternative that assists businesses with understaffed or under-skilled IT teams delivering superior private cloud services and infrastructure.
- Clouds with a specific purpose (Dedicated Clouds)
There’s a cloud within a cloud. A dedicated cloud might be on a public cloud (for example, Red Hat OpenShift® Dedicated) or a private cloud. An accounting department, for example, may have its specialized cloud within the company’s private cloud.
- Hybrid Clouds
A hybrid cloud is a unified IT system of several environments linked through LANs, WANs, VPNs, and APIs.
Hybrid cloud features are complicated, and the criteria vary depending on who you ask. A hybrid cloud, for example, could need to include the following:
- There must be at least one private cloud and one public cloud.
- at least two private clouds
- at least two public clouds
- At least one public or private cloud linked to a bare-metal or virtual environment
When apps can move in and out of various separate—yet connected—environments, any IT system becomes a hybrid cloud. At least a couple of those environments must be provided from centralized IT resources that can scale up and down as needed. And utilizing an integrated management and orchestration platform, all of those environments must be controlled as a single environment.
- Multi-cloud
Multi-cloud is a cloud architecture that combines many cloud services from multiple cloud vendors, whether public or private. Not all multi-clouds are hybrid clouds, and not all hybrid clouds are multi-clouds. When various clouds are coupled through integration or orchestration, they become hybrid clouds.
A multi-cloud environment may exist on purpose (to manage sensitive data better or as redundant storage space for enhanced disaster recovery) or by accident (to better control sensitive data or as redundant storage space for improved disaster recovery) (usually the result of shadow IT). In any case, having numerous clouds is becoming increasingly prevalent among businesses looking to increase security and performance by diversifying their environments.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is no longer a new idea trying to catch on; it has evolved into a necessary business tool. By understanding the importance of cloud computing in business and how it can be tailored to your specific needs, you can improve workplace efficiency, collaboration, and security. Are you ready to take your business a level up? Contact us today, and we will show you how the cloud can work for you.
Abhinav Sathyamurthy is a professional blogger with over six years of experience covering technical topics such as blockchain, ERP, AI, and other matters.


